Bitrates
A bitrate is the number of bits conveyed or transferred in a unit of time. When talking about music formats, bitrate is used in kilobits per second (kbps). When comparing files with different bitrates (of the same song), the file with the higher bitrate has the higher quality. For example, an MP3 320kbps (CBR) file transfers 320 kilobits per second.
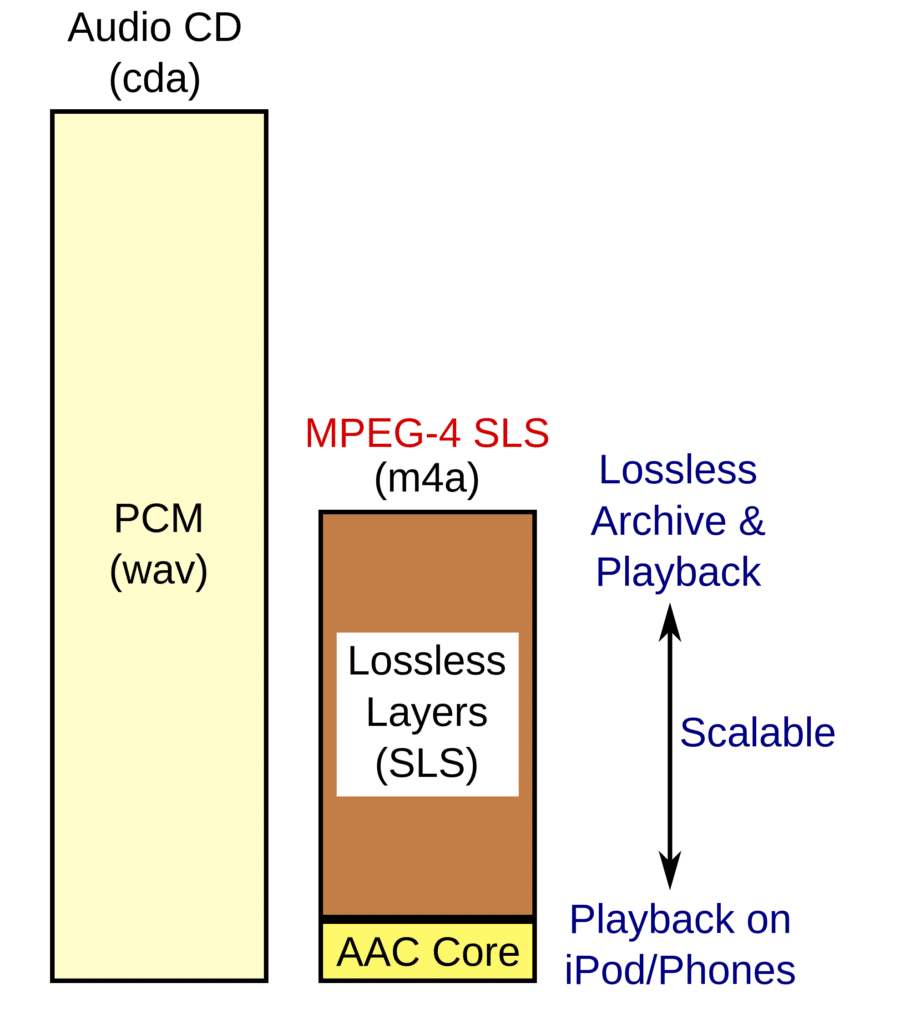
Uncompressed Lossless
Uncompressed lossless formats store all of the original recorded data. Since silence is given the same number of bits per second as sound is, uncompressed lossless files are huge. The main uncompressed lossless format is pulse-code modulation (PCM). For example:
- WAV (PCM) (used on Windows)
- AIFF (PCM) (used on macOS)

Compressed Lossless
Compressed lossless formats store all of the original recorded data in less space than uncompressed lossless formats by compressing the data. By giving silence almost no bits per second and compressing sound, a compressed lossless file is usually half as big as the same song stored in an uncompressed lossless file.
Since both uncompressed lossless formats and compressed lossless formats retain all the data from the original recording, they can be transcoded between each other without a loss in quality. For example:
- Free Lossless Audio Codec (FLAC)
- Apple Lossless Audio Codec (ALAC)
- Monkey's Audio (APE)
Lossy
Lossy formats are always compressed. Lossy formats have smaller file sizes than both uncompressed lossless formats and compressed lossless formats because they remove some of the original data. Usually the removed data is in the higher frequencies that humans can't hear, however, there can be obvious audible differences between lossy formats and lossless formats.
Lossy formats CANNOT be transcoded into any other lossy format without losing more quality. It CANNOT be transcoded into lossless either, because it wouldn't be a true lossless file when the source medium is already lossy. Examples of lossy formats include:
- MPEG Layer 3 Audio (MP3)
- Advanced Audio Encoding (AAC)
- Windows Media Audio (WMA)
- Dolby Digital Audio Codec 3 (AC3)
- DTS Coherent Acoustics Codec (DTS)

File size
How big your audio file will be depends on the length of the audio as well as its bitrate. When the files are stored on disk, they take up a certain amount of space, the actual storage space needed is measured in bytes (or megabytes/gigabytes for larger files).
- Uncompressed Lossless — WAV (PCM): 34.3 MB
- Compressed Lossless — FLAC: 25.75 MB (25% compressed)
- Lossy — MP3 320 (CBR): 7.78 MB (78% compressed)

Transparency
Transparency is a term used to describe the audible quality of a lossy music file. A lossy file is considered transparent if the average human cannot tell the difference between the lossy file and a lossless file of the same song by just listening to both without knowing which file is which. For most people, MP3 192kbps (CBR) is considered transparent.

Spatial Audio
Dolby Atmos
Dolby Atmos (EC-3/EAC3-JOC) is an advanced audio technology that allows sound to be precisely placed and moved in three-dimensional space, including overhead. It extends the concept of surround sound with added height channels, providing a more immersive audio experience.

Dolby Digital
Dolby Digital (also known as AC-3/AC-4 IMS) is a digital audio coding standard that compresses audio data to reduce the amount of space needed for storage and transmission. It is commonly used in DVDs, Blu-rays, and broadcast television.
Sony 360 Reality Audio
Sony 360 Reality Audio (MHM1/MHA1) is an immersive audio format that uses object-based spatial audio technology to create a 360-degree sound field. This format aims to recreate the experience of being at a live concert or in a recording studio with sound coming from all directions.

Binaural Audio
Binaural audio is a method of recording sound that uses two microphones arranged to create a 3D stereo sound sensation for the listener. This recording technique is designed to mimic the way human ears hear, with the microphones placed at a distance that simulates the human head.

Downmix
Downmixing is the process of converting a multi-channel audio track (such as 5.1 or 7.1 surround sound) into a format with fewer channels (such as stereo or mono).